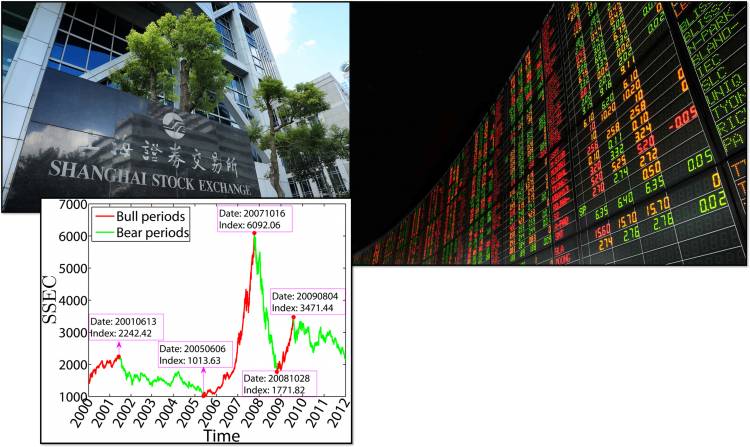
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE): ups and down: Main Stock Exchange in the world
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE): ups and down
Here’s a detailed overview of the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE):
Table of Contents
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE): ups and down. 1
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) Impression. 2
2. State-Guided but Market-Oriented. 2
4. Limited Foreign Access (but growing) 3
1. Economic Allegations (Domestic & Global) 3
2. Financial Market Implications. 4
3. Geopolitical and Strategic Implications. 4
4. Corporate Governance Implications. 4
Foreign Access & Link Programs: 8
If you'd like, I can also provide: 9
Short Summary: Ups and Downs of SSE. 10
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) Impression
Basic Information:
- Full Name: Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
- Chinese Name: 上海证券交易所
- Founded: November 26, 1990
- Commenced Operations: December 19, 1990
- Location: Lujiazui, Pudong, Shanghai, China
- Website: www.sse.com.cn
Implication:
- One of Two Main Mainland Exchanges: Along with the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE).
- Largest in China by total market capitalization.
- Top 3 in Asia, Top 5 globally by market cap (as of recent rankings).
- Operates under the supervision of the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC).
The implications of the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) are wide-ranging and impact not just China’s economy, but also global markets. Here's a breakdown of its key implications across different dimensions:
More info about SSE Impression...
Impression of the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
The Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) is one of the most influential and largest stock exchanges in the world, playing a vital role in China's economic engine and global finance. It represents a blend of state-led capitalism and market-driven finance, making it unique among major global exchanges.
Essential Impression & Features
1. Size & Effect
- One of the top 5 largest stock exchanges by market capitalization globally.
- Home to many of China’s biggest state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and private giants (e.g., PetroChina, ICBC, SAIC).
Impression: A powerful financial hub with massive market depth and growing international influence.
2. State-Guided but Market-Oriented
- The SSE operates with strong government oversight, but allows a free-market mechanism in pricing and trading.
- Reflects China’s dual-track model: government direction + capital market liberalization.
Impression: A hybrid system: planned, stable, but less elastic than fully free-market exchanges.
3. Split Market Assembly
- Divided into two main boards:
- Main Board: For large, established companies.
- STAR Market: A tech-heavy, Nasdaq-style board absorbed on innovation, launched in 2019.
Impression: SSE is actively modernizing to support high-growth sectors like tech, biotech, and AI.
4. Limited Foreign Access (but growing)
- Historically closed to international savers.
- Programs like Stock Connect (with Hong Kong) and QFII/RQFII have gradually opened access.
Impression: Becoming more open to global capital, but still under watchful regulation.
5. Instability and Gossip
- SSE has been known for episodes of sharp market swings, often driven by retail investors and rule shifts.
- Government occasionally intervenes during market turbulence.
Impression: Volatile and policy-sensitive, yet with enormous potential.
Rapid Impression
The Shanghai Stock Exchange is a massive, evolving financial powerhouse, reflecting China's complex mix of centralized preparation and market drive. It's modernizing rapidly and becoming more globally integrated, but still operates under a unique set of rules influenced by state strategy, saver sentiment, and improvement pace.
1. Economic Allegations (Domestic & Global)
For China:
- Capital Raising Platform: Enables Chinese companies, especially large state-owned enterprises (SOEs), to raise funds for growth.
- Economic Development: Fuels innovation (especially through the STAR Market for tech firms), supporting China’s shift from a manufacturing-based economy to a high-tech economy.
- Wealth Creation: Gives individuals and institutions access to investment opportunities, promoting domestic wealth accumulation.
- Monetary Policy Tool: Reflects investor confidence and acts as a barometer for China’s economic health.
For the World:
- Gateway to China’s Economy: SSE-listed companies provide insights into China’s industrial, financial, and tech sectors.
- Investment Destination: Attracts foreign institutional investors through Stock Connect and QFII programs.
- Supply Chain Signals: SSE performance influences global commodity and manufacturing supply chains (e.g., steel, semiconductors, EVs).
2. Financial Market Implications
- Global Integration: The Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect and China’s inclusion in global indexes (e.g., MSCI, FTSE) increase exposure to Chinese assets.
- Volatility Impact: Unexpected drops or rallies in SSE can send shockwaves through global fairness and currency markets, especially emerging markets and commodities.
- Liquidity Provider: With high daily trading volumes, SSE contributes significantly to Asia’s capital market liquidity.
3. Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
- Financial Sovereignty: Firming domestic exchanges like SSE reduces China’s reliance on foreign capital market places.
- Tech Independence: The STAR Market is key to Beijing’s goal of fostering homegrown tech giants (seen as an answer to NASDAQ).
- Soft Power: Promoting the yuan-denominated capital market enhances China’s influence in global finance.
4. Corporate Governance Implications
- Better-quality Transparency: Public listings require disclosures and audits—encouraging better corporate governance among Chinese firms.
- Market Correction: Investors influence company behaviour via stock performance, pushing for higher efficiency and accountability.
5. Risks and Concerns
- Government Interference: SSE is known for state influence; authorities may suspend IPOs or trading to stabilize the market.
- Selling Domination: A high proportion of retail traders increases volatility and speculation.
- Controlling Uncertainty: Shifts in government policy can suddenly affect investor sentiment and valuation.
Instant of Implications
|
Domain |
Implication |
|
Economy |
Energies growth, tech innovation, and capital allocation in China |
|
Finance |
Affects global markets, offers investment routes into China |
|
Geopolitics |
Boosts China’s financial autonomy and planned influence |
|
Corporations |
Encourages better governance, transparency |
|
Investors |
Presents high-reward but high-risk opportunities |
Market Structure:
The SSE does not use a floor trading system—it’s fully electronic. It offers different markets:
1. Key Board:
- For large, recognised companies.
- Includes many state-owned enterprises (SOEs).
2. STAR Market (科创板):
- Launched in July 2019.
- Modelled after NASDAQ.
- Focuses on science and technology innovation companies (e.g., biotech, AI, semiconductors).
- Has relaxed IPO rules and a registration-based IPO system.
Securities Traded Types:
- A-shares: RMB-denominated shares for domestic investors.
- B-shares: USD-denominated, mainly for foreign investors (less popular today).
- Bonds: Government, company, and exchangeable bonds.
- Funds: ETFs, closed-end funds, etc.
More info about types...
Types of Securities Traded on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
1. A-Shares
- Description: Stocks of companies incorporated in mainland China, traded in Renminbi (CNY).
- Investors: Primarily domestic investors, but open to qualified foreign investors via programs like QFII, RQFII, or Stock Connect.
- Most Common Security Type on SSE.
2. B-Shares
- Description: Shares of companies based in mainland China, but traded in foreign currencies (USD on SSE).
- Investors: Open to foreign investors; now rarely used due to liberalization of A-shares.
- Less active than A-shares; considered legacy securities.
3. Bonds
Various types of bonds are traded on the SSE:
|
Type |
Description |
|
Government Bonds |
Issued by the central government of China. |
|
Corporate Bonds |
Issued by listed and unlisted companies. |
|
Enterprise Bonds |
Issued by large state-owned enterprises. |
|
Convertible Bonds |
Bonds that can be converted into shares. |
4. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Definition: Funds that track a specific index (like SSE 50 or CSI 300) and trade like stocks.
- Benefits: Diversification, transparency, low cost.
- Growing in popularity among both retail and institutional investors.
5. Closed-End Funds
- Definition: Funds that matter a fixed number of shares and are traded on the exchange.
- Different from ETFs: These are actively managed and may trade at a discount or premium to their net asset value.
6. REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts)
- Launched: First batch in 2021.
- Purpose: Allow investment in infrastructure and real estate projects, such as highways, industrial parks, and logistics hubs.
- Status: Still emerging, but a growing part of the market.
7. Depository Receipts (CDRs)
- Definition: Chinese Depository Receipts represent ownership in overseas-listed companies (like Alibaba, which is listed in the U.S.).
- Goal: Encourage tech companies to “come home” and list domestically.
8. STAR Market Securities (科创板)
- A sub-market under SSE for:
- High-tech, biotech, semiconductors, AI, clean energy, etc.
- Trades mainly A-shares but with different IPO and trading rules:
- Registration-based IPO system
- No profit requirement for listing
- More flexible price limits (e.g., ±20%)
Summary Table
|
Security Type |
Currency |
Investor Type |
Key Notes |
|
A-Shares |
RMB |
Domestic & Qualified Foreign |
Most common |
|
B-Shares |
USD |
Foreign |
Legacy market |
|
Bonds |
RMB |
All |
Includes gov’t, corporate, convertible |
|
ETFs |
RMB |
All |
Index-based, liquid |
|
Closed-End Funds |
RMB |
All |
Fixed capital funds |
|
REITs |
RMB |
All |
Infrastructure-based |
|
CDRs |
RMB |
All |
Overseas company exposure |
|
STAR Market Shares |
RMB |
All |
Tech & innovation-focused |
Foreign Access & Link Programs:
Foreigners traditionally had limited access, but recent reforms improved access:
- QFII / RQFII Programs: Allow qualified foreign institutions to invest.
- Stock Connect (since 2014):
- Shanghai–Hong Kong Stock Connect: Enables foreign investors to buy eligible SSE shares via Hong Kong.
- Enhances global integration of China's capital market.
Indexes:
Some main indices under the SSE:
|
Index |
Description |
|
SSE Composite Index |
Tracks all stocks (A & B shares) on SSE. |
|
SSE 50 Index |
50 largest companies by market cap and liquidity. |
|
SSE 180 Index |
Broader representation of large and mid-cap companies. |
|
STAR 50 Index |
Top 50 tech firms on the STAR Market. |
Rule & Mistake:
- Regulated by the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC).
- Implements T+1 settlement for A-shares (you buy today, sell tomorrow).
- Uses price fluctuation limits (typically ±10%) to curb volatility.
Notable Listed Companies:
- PetroChina
- Sinopec
- Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC)
- China State Construction
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. (CATL): on STAR Market
Future Viewpoint:
- Focus on opening up to global investors.
- Push to list more tech and innovation-driven companies.
- Increased international recognition due to China’s economic influence.
If you'd like, I can also provide:
- Charts or historical data
- Comparison with other exchanges (like NASDAQ or HKEX)
- Insights into investing as a foreigner
Let me know!
“When do markets open”
Here are the market hours for the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE):
- Shanghai Stock Exchange Trading Hours (China Standard Time - CST)
- Monday to Friday (except public holidays)
|
Session |
Time |
|
Pre-market Session |
09:15 AM – 09:25 AM |
|
Opening Call Auction |
09:15 AM – 09:25 AM |
|
Continuous Trading (Morning) |
09:30 AM – 11:30 AM |
|
Lunch Break |
11:30 AM – 01:00 PM |
|
Continuous Trading (Afternoon) |
01:00 PM – 03:00 PM |
Noted that:
- T+1 system: You can only sell shares the day after purchase.
- No weekend trading
- Public holidays: The market is closed on major Chinese holidays (e.g., Lunar New Year, National Day).
Short Summary: Ups and Downs of SSE
The Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) is one of the world’s major and most significant stock markets, reflecting China’s economic power. Over the years, it has seen significant ups and downs:
Ups points:
- Rapid Growth: Hosts China’s chief businesses like ICBC, PetroChina, and high-tech firms on the STAR Market.
- World-wide Influence: Among the top exchanges by market capitalization.
- Modernization: Launch of the STAR Market and increased foreign investor access via Stock Connect programs.
Downs points:
- Volatility: Known for affected market swipes, such as the 2015 crash.
- Policy Dependence: Strong government influence creates unpredictability.
- Limited Transparency: Compared to Western exchanges, it faces issues with regulatory openness.
My Overall view, SSE is a fast-growing but state-influenced exchange, combination strong potential with exclusive challenges.