Benefits of Chia Seeds for Weight Loss and other Uses
Benefits of Chia Seeds for Weight Loss and other Aids
Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica) are the small, oval seeds of a flowering plant in the mint family, native to Central America. Scorn their small size, they are considered a source of food, as they contain fibber, protein, healthy fats, and essential micronutrients. Below is a detailed description of the benefits of chia seeds, backed by science and old-style use:
Table of Contents
Benefits of Chia Seeds for Weight Loss and other Aids. 1
Nutritional Profile (per 28g / 2 tablespoons) 1
Health Benefits of Chia Seeds. 1
1. Chia Seeds: Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids. 1
2. High in fibber (supports digestion and gut health) 3
4. Helps control blood sugar levels. 5
5. Promotes weight loss and satiety. 5
7. Boosts Energy and Endurance. 6
9. Good Source of Plant-Based Protein. 6
10. May Reduction Inflammation. 7
How to Add Chia Seeds to Your Diet 7
Protections & Considerations. 7
If you'd like, I can also offer: 8
Chia Seed Plant Description. 8
???? Chia Seed Plant: Salvia hispanica. 8
???? Scientific Classification. 8
Where is chia plant grown today?. 10
Can you grow chia at home?. 10
In which country do people consume the most chia seeds?. 11
Top countries that consume the most chia seeds. 11
________________________________________________
Nutritional Profile (per 28g / 2 tablespoons)
- Calories: ~138
- Fiber: 10-11 grams (40% of the Daily Value)
- Protein: 4-5 grams
- Fat: 9 grams (mainly omega-3 ALA)
- Calcium: 18% DV
- Magnesium: 23% DV
- Phosphorus: 27% DV
- Zinc, potassium, B vitamins
________________________________________________
Health Benefits of Chia Seeds
1. Chia Seeds: Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
One of the most remarkable nutritional benefits of chia seeds is their high content of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) — an essential fat that plays a key role in brain, heart, and cellular health.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids crucial for health. The three main types are:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) – found in plants like chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts.
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) – found in fish oil.
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) – also found in fish oil and seaweed.
ALA is essential because the human body can’t produce it — it must come from food.
Omega-3 Content in Chia Seeds
- One ounce (28 grams) of chia seeds contains:
- ~5 grams of ALA omega-3 fatty acids
- This is more than salmon (per gram) for ALA content (but salmon has EPA/DHA)
Chia seeds are among the richest plant-based sources of omega-3s — ideal for vegetarians, vegans, and people avoiding fish.
Health Benefits of ALA in Chia Seeds
1. Brain Health
- Supports brain cell membrane structure
- May help protect against neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, dementia)
- Improves mood and focus (ALA is linked to reduced depression risk)
2. Heart Health
- Reduces inflammation in arteries
- Helps lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol
- Improves blood vessel function
- Supports healthy heart rhythms
Studies show that ALA may reduce the risk of cardiovascular sicknesses by 10–20%.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- ALA helps calm chronic inflammation, which is at the root of many modern diseases (e.g., arthritis, type 2 diabetes, heart disease).
4. Cellular Protection
- Omega-3s are crucial for maintaining cell membrane flexibility and function
- Promotes skin hydration and elasticity
How to Maximize Omega-3 Intake from Chia Seeds
- Soak the seeds before eating – this improves digestion and absorption
- Combine with other omega-3 rich foods: walnuts, flaxseeds, seaweed, leafy greens
- Take with a small amount of healthy fat (e.g., coconut oil, olive oil) for better absorption
Note on ALA Conversion
While chia seeds are high in ALA, the body only converts a small portion to EPA and DHA, the more bioavailable forms. Factors affecting conversion:
- Age, gender (women may convert better), health status, diet
If you're relying solely on chia for omega-3s, consider:
- Algae-based omega-3 supplements for DHA/EPA (vegan-friendly)
- Including other plant-based omega-3 sources
Summary of Omega-3
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Omega-3 Type |
ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) |
|
Content per 28g serving |
~5g ALA |
|
Benefits |
Brain, heart, anti-inflammation, skin |
|
Ideal For |
Vegans, vegetarians, heart-conscious |
|
Note |
ALA conversion to EPA/DHA is limited |
Would you like a comparison chart of omega-3 content in different seeds (chia, flax, hemp)? Or a list of vegan omega-3-rich meals using chia seeds?
________________________________________________
2. High in fibber (supports digestion and gut health)
Chia seeds contain 40% fibber by weight, making them one of the best sources of fibber available.
- Inexplicable and soluble fibber helps regulate bowel movements.
- Helps prevent constipation.
- Acts as a prebiotic, feeding healthy gut bacteria.
- Slows digestion and supports blood sugar balance.
________________________________________________
3. Supports heart health.
Chia Seeds and Heart Health: A Closer Look
Chia seeds are widely considered a heart-healthy superfood. Thanks to their unique combination of omega-3 fatty acids, fibber, antioxidants, and plant-based protein, they offer a host of benefits that directly support circulatory health.
How Chia Seeds Support Heart Health
1. Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids (ALA)
Chia seeds are an excellent plant-based source of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a type of omega-3 fatty acid.
ALA helps:
- Reduce inflammation in the arteries
- Lower blood pressure
- Improve cholesterol balance
- Prevent blood clotting
- Scientific evidence suggests that ALA may reduce the risk of heart disease by improving arterial function.
- Observational studies have linked ALA intake with a 10–20% lower risk of fatal heart disease.
2. High in soluble fibber
Chia seeds are packed with soluble fibber (about 10 grams per 2 tablespoons), which:
- Helps lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol.
- Combines with bile acids to remove excess cholesterol from the body.
- Slows down carbohydrate digestion, stabilizing blood sugar—important for preventing heart disease.
3. Powerful antioxidants
Chia seeds contain:
- Quercetin
- Chlorogenic acid
- Caffeic acid
- Kaempferol
These compounds combat oxidative stress and protect blood vessels from damage, which is important for preventing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
4. Supports healthy weight management.
Excess weight and abdominal fat are major risk factors for heart disease.
Chia seeds help with:
- Satisfaction (due to fiber and protein)
- Reducing appetite
Stabilizing blood sugar and insulin levels.
By helping with weight loss or maintenance, chia seeds indirectly protect heart health.
5. Helps regulate blood pressure.
A small study found that people with high blood pressure who consumed chia seeds experienced a slight decrease in their systolic blood pressure.
The omega-3 and magnesium content helps relax blood vessels and improve circulation.
6. Plant-Based Protein for Vascular Health
Chia contains all 9 essential amino acids, which support:
- Tissue repair
- Muscle function (including heart muscle)
- Metabolism regulation, reduction of cardiovascular stress
Scientific Support
Some notable studies:
- British Journal of Nutrition (2009): Chia consumption reduced triglycerides and increased HDL ("good") cholesterol.
- Diabetes Care (2007): Chia helped improve blood pressure and inflammatory markers in diabetic patients.
- Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (2014): Daily chia consumption improves omega-3 levels and reduces inflammation.
Summary Table
Benefits of Chia for the Heart
- Omega-3 ALA reduces inflammation and promotes circulation.
- Soluble fibber reduces LDL and stabilizes blood sugar. Antioxidants protect blood vessels from oxidative damage. Protein (complete protein) maintains heart muscle and metabolism. Magnesium and potassium control blood pressure. Fiber, which promotes satiety, helps control weight and cholesterol.
The Best Ways to Eat Chia for Heart Health
- Chia Water (soak 1 tablespoon of chia in 1 glass of water)
- Chia Pudding (with unsweetened almond milk and berries)
- Add to smoothies, oatmeal, or yogurt.
- Use it in whole-grain baked goods or sprinkle it on salads.
________________________________________________
4. Helps control blood sugar levels.
When chia seeds are soaked, they form a gel-like substance that slows the absorption of sugar into the blood.
- Useful for diabetics or pre-diabetics.
- May help improve insulin sensitivity.
________________________________________________
5. Promotes weight loss and satiety.
Because of these:
- High fibber content (keeps you feeling fuller longer)
- Protein content (reduces appetite)
- Ability to absorb water (can absorb up to 12 times its weight)
They help stop overeating and reduce cravings.
- A study shows that people who eat chia seeds in yogurt feel fuller for longer, leading to fewer calories afterward.
6. Supports Bone Health
Chia seeds are rich in:
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Protein
These are essential for strong bones, teeth, and preventing osteoporosis, particularly for people who avoid dairy.
7. Boosts Energy and Endurance
Historically, Aztec warriors consumed chia seeds for energy and stamina.
Current educations show:
- Steady release of energy (due to slow-digesting fibber)
- Reduced post-exercise inflammation
- Electrolyte balance support (magnesium and potassium)
8. Rich in Antioxidants
Chia seeds contain chlorogenic acid, quercetin, and caffeic acid, which:
- Fight free radicals
- Slow down aging
- Protect cells from oxidative stress
- Support skin health and reduce wrinkles
9. Good Source of Plant-Based Protein
Chia seeds provide all 9 essential amino acids (a whole protein).
- Great for vegans and vegetarians
- Supports muscle repair and growth
- Helps control blood sugar and hormones
10. May Reduction Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Swelling
Chia’s omega-3s and antioxidants help fight low-grade, chronic irritation in the body.
How to Add Chia Seeds to Your Diet
Chia seeds are tasteless, making them extremely versatile:
- Soaked in water/milk (chia sweet)
- Added to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal
- Used as a vegan egg substitute (1 tbsp chia + 3 tbsp water = 1 egg)
- Mixed in baked goods (bread, muffins)
- Stirred into salad dressings or sauces
- Topped on fruit bowls or cereals
Memo: Always soak or mix with liquid before incontrollable large amounts to avoid digestive discomfort or choking risk.
Protections & Considerations
- Start small: Some people may experience bloating or gas.
- Drink plenty of water when consuming chia.
- Rarely, some may be allergic.
- Chia can interact with blood thinners or blood pressure meds — consult your doctor if concerned.
Summary Bench
|
Benefit |
Key Component(s) |
Outcome |
|
Omega-3 Source |
ALA |
Brain + heart health |
|
High Fiber |
10g per serving |
Digestion, weight control |
|
Antioxidants |
Quercetin, chlorogenic |
Anti-aging, cell protection |
|
Bone Health |
Calcium, magnesium |
Prevents bone loss |
|
Satiety |
Gel-forming fiber |
Reduces appetite |
|
Protein |
9 essential amino acids |
Muscle growth, vegan-friendly |
|
Blood Sugar Support |
Soluble fibber |
Balanced energy |
|
Anti-Inflammatory |
Omega-3, flavonoids |
Less joint pain, chronic disease |
If you'd like, I can also offer:
- Sample chia recipes (puddings, smoothies, breads)
- A weekly chia meal plan
- Infographic of chia seed benefits
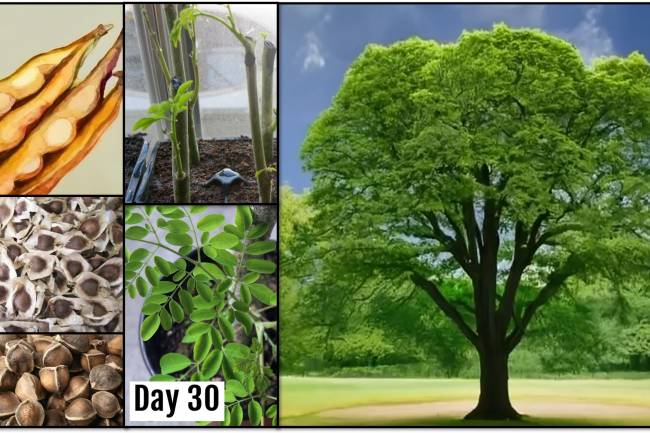
Chia Seed Plant Description
Here is a detailed description of the chia seed plant (Salvia hispanica), from its botanical origin to how it is grown and used.
???? Chia Seed Plant: Salvia hispanica
???? Scientific Classification
Category Description
- Common Name: Chia
- Botanical Name: Salvia hispanica
- Family: Lamiaceae (Mint Family)
Native to Central America (Mexico, Guatemala)
Type: Herbaceous flowering plant.
Annual (completes its life cycle in one season)
Plant Description
- Height: 3-5 ft (90-150 cm)
- Leaves: Dark green, opposite, oval leaves with serrated edges; light-haired and fragrant.
- Stems: Square stems typical of the mint family.
- Flowers: Small, tubular, purple or white flowers clustered in spikes, about 3 to 4 inches long.
- Seeds:
- Small (1–2 mm), oval
- Colour: Black, brown, Gray, or white.
- Glossy, hard outer casing.
Growing Conditions
- Climate
- Warm-season plant; thrives in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Long daylight hours and temperatures between 20 and 30°C (68 and 86°F) are required.
- Frost-sensitive.
Sunlight
- Full sun (at least 6–8 hours per day)
Soil
- Well-drained, sandy or loamy soil
- Prefers a pH between 6.0 and 8.5.
- No heavy fertilizer is needed.
Irrigation
- Drought tolerant once established.
- Moderate watering is required during initial growth
Flower and Seed Production
- Chia is photoperiod-sensitive: it begins to flower when daylight is less than about 12 hours.
- It is grown primarily for its seeds, which are harvested after the flower has dried.
Growing Timeline
- Sowing to Harvest: ~100-150 days
- Sowing Time: Spring (after frost)
- Harvest Time: Late summer or early fall.
Harvesting Chia Seeds
- Wait until the flower heads are dry and brittle.
- Cut the stems and dry them in a shady location.
- Thresh the flower heads to extract the seeds.
- Clean and store in airtight containers, away from moisture and light.
Where is chia plant grown today?
Commercially grown:
- Mexico (homeland)
- Argentina
- Bolivia
- Peru
- Paraguay
- Australia
- India (parts of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu)
- Gaining popularity worldwide due to health claims.
Fun Facts
- Chia was a staple food of the Aztecs and Mayans: the word "chia" means "strength" in the Mayan language.
- The seeds can absorb 10 to 12 times their weight in water and form a gel that aids hydration.
- It is also used in traditional medicine to increase energy and stamina.
Chia plant vs. Flax plant
Characteristics: Chia (Salvia hispanica) Flax (Linum eutecticum)
- Seed size: small, large
- Source of Omega 3 (ALA)
- Plant height: 3–5 feet
- 2–4 feet
- Soil tolerance: Rich in sandy/loamy soil, well-drained.
- Uses: seeds, oils, sprouted seeds, oils, fibber.
Can you grow chia at home?
- Yes! Here's the method:
- Start indoors in small pots or directly outdoors during warm weather.
- Sow seeds shallowly in well-drained soil.
- Water moderately and place in full sun.
- Once the plants are tall, stake them if necessary.
- Harvest seeds when the flower heads are brown and dry.
In which country do people consume the most chia seeds?
Today, chia seeds are consumed worldwide, but their popularity is greatest in a few specific countries, primarily due to health consciousness and modern dietary trends such as veganism, keto, and clean eating.
Below is a detailed look at which countries consume the most chia seeds and why:
Top countries that consume the most chia seeds.
United States
- The largest consumer of chia seeds globally.
Popular in:
- Health food stores, supermarkets
- Smoothies, puddings, protein bars, granola
Driven by:
- High demand for plant-based, gluten-free, and fiber-rich foods.
- Dietary trends such as paleo, vegan, and keto
- Chia seeds are now a popular superfood in the US health and fitness market.
Canada
- A strong health food culture like the US
- Widely used:
- Breakfast foods (oatmeal, cereal)
- Homemade snacks and baked goods
- Popular among vegetarians, vegans, and athletes.
Australia
Increasing consumption due to a strong focus on clean eating and natural health.
- Australia also grows chia, particularly in Western Australia (Kanunnora region).
- Generally:
- Health stores
- "Superfood" blends
- Wellness recipes.
United Kingdom
Due to growing popularity:
- Wellness movement
- Focus on gut health and weight loss.
- It is used in porridges, smoothies, breakfasts, and pastries.
Germany
Strong organic and bio food culture.
- Chia is used in:
- Muslim
- Vegan recipes.
- Artisan breads
- Regulated by the EU as a "novel food," meaning it must be properly labeled and approved.
India (increasing use)
Not traditionally used, but now gaining popularity in:
- Urban areas
- Health-related, among fitness enthusiasts
- Chia seeds are locally known as "sabja" (although technically sabja comes from basil, not chia).
- Used in:
- Detox water
- smoothies
- Weight loss foods
- Ayurvedic-inspired health drinks
Other included countries:
Brazil and Mexico: Chia's traditional roots are still widely used in foods and beverages like chia water.
Japan and South Korea: Superfood consumption is a growing trend among health-conscious people.
Middle East (UAE, Qatar): High usage among expats and societies with modern lifestyles.
Summary points
- Country popularity in general use
- USA: Many smoothies, bars, bowls, keto diets
- Canadian vegan foods, protein snacks, and baked goods
- Australia: High + Local farm chia puddings, cereals, agriculture
- UK: Medium – High: Porridge, Breads, Smoothies
- Germany: Medium-High artisan breads, organic products
- India is growing rapidly in detox drinks, weight loss, and modern recipes.
- Traditional Mexican use of Chia Water, a health tonic